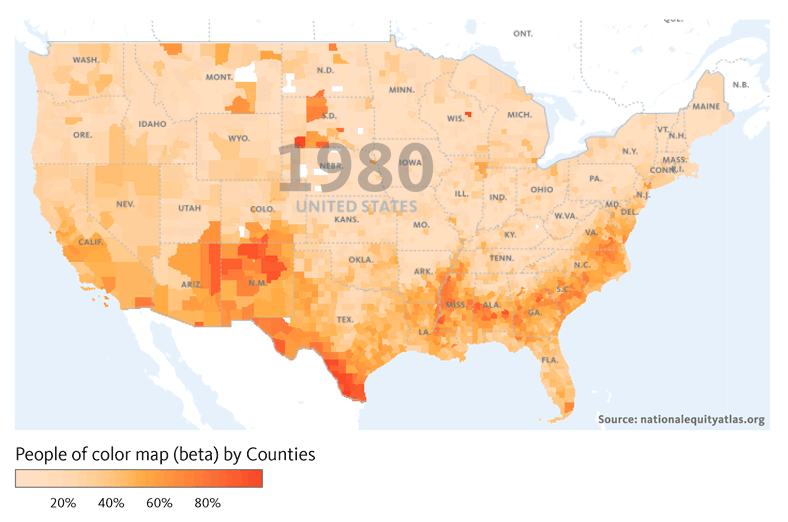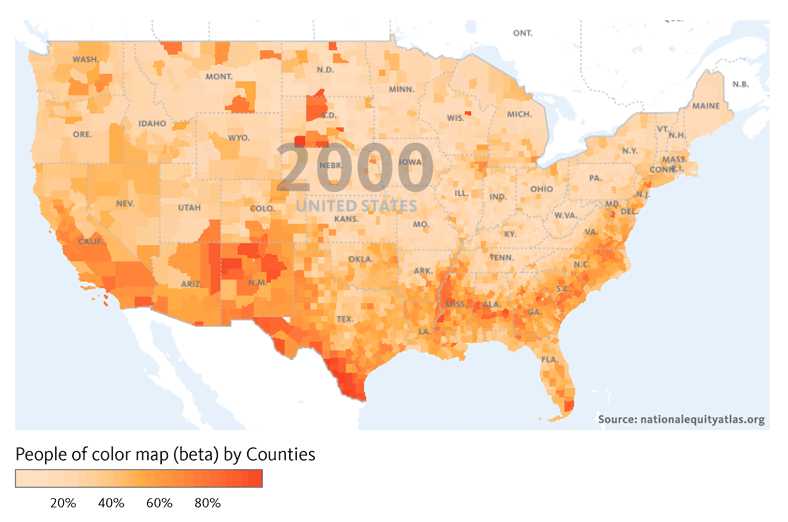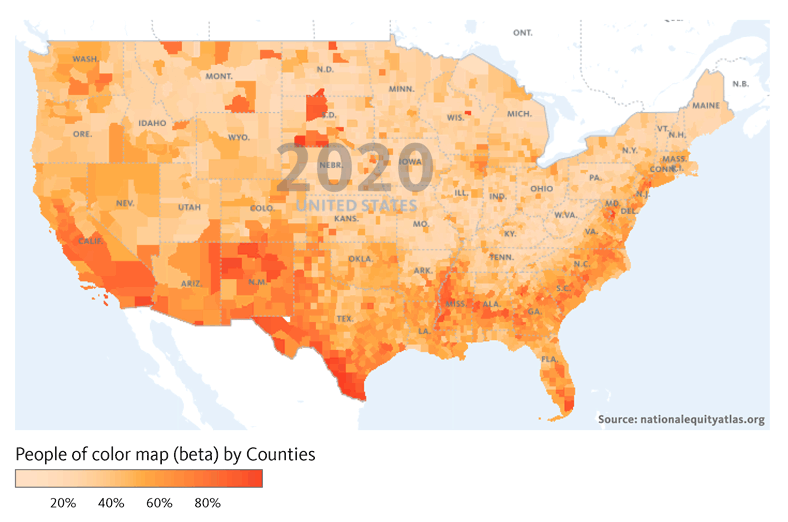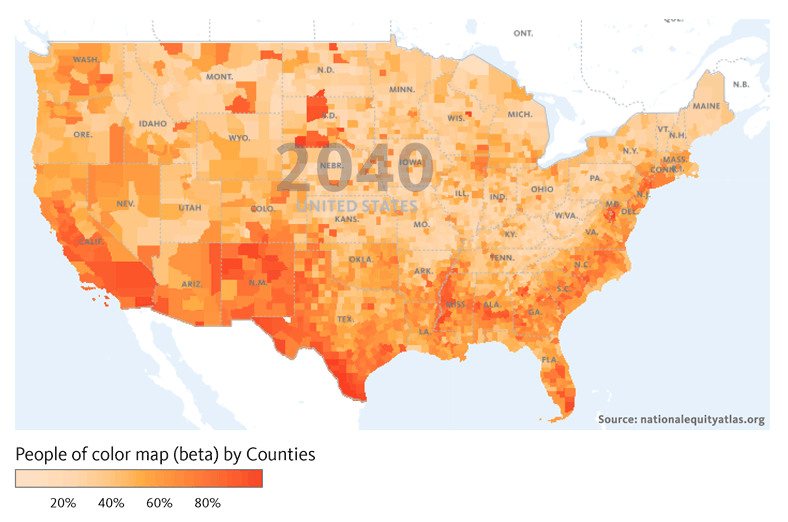
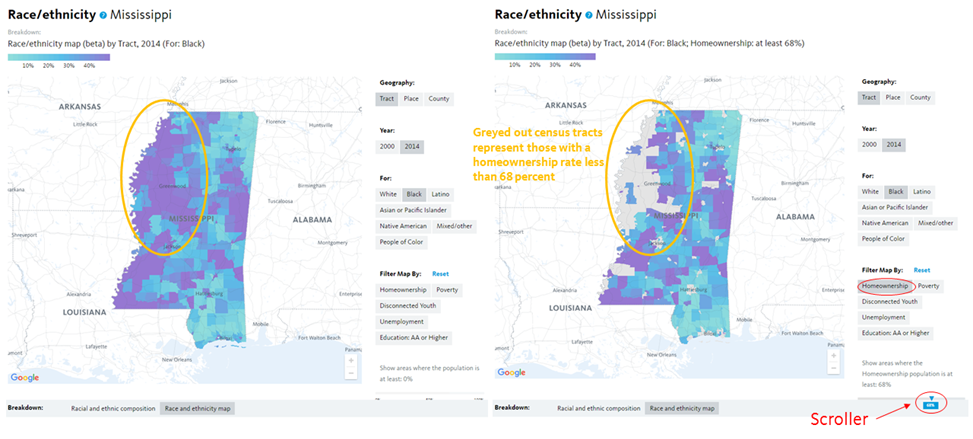
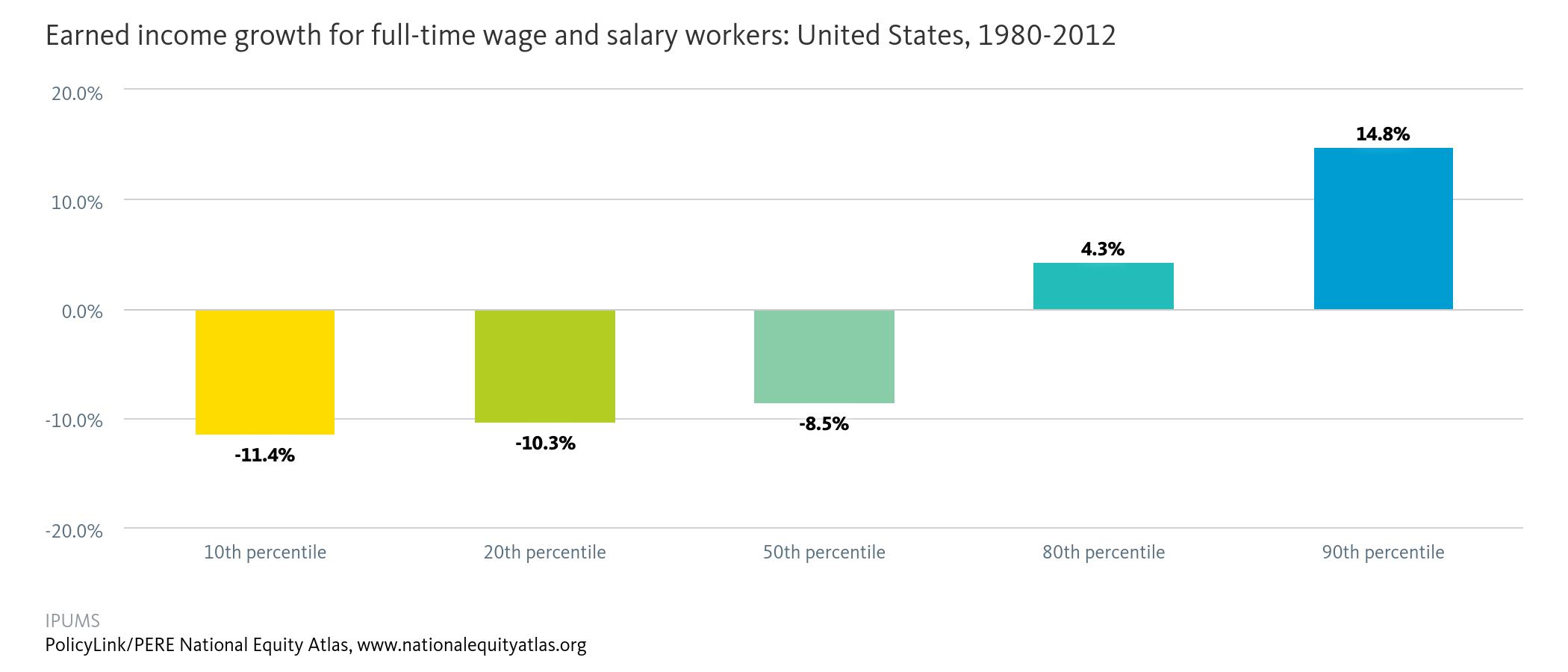
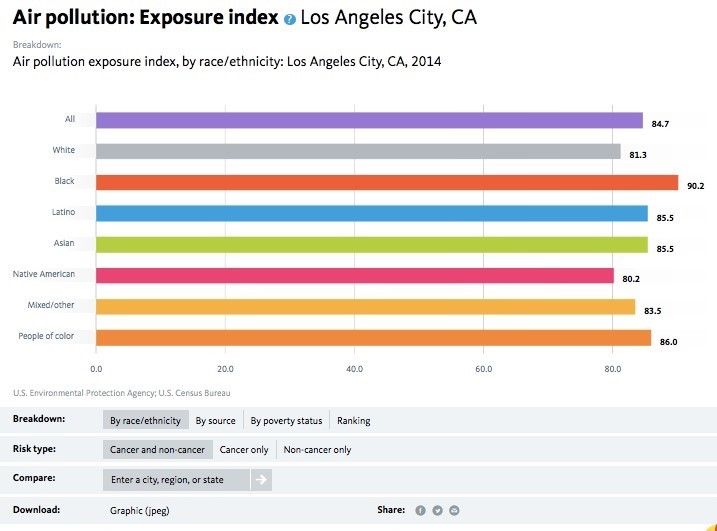
Financial institutions have a long history of failing to meet the needs of low-income communities and communities of color — whether through discriminatory practices that strip wealth from neighborhoods of color or systematic disinvestment that has left too many struggling communities without access to affordable banking.
Over the past few years, however, community advocates have been putting an established advocacy tool to new use to bring the voices and needs of underserved communities to the negotiating table with local banks.
Community benefits agreements (CBAs) — contracts that have traditionally been used to ensure that local real estate development projects create opportunities for local workers and communities — are increasingly being applied to banks to increase access to financial services for disadvantaged communities.
"Banks have an important role to play in our communities, and these community benefits agreements help ensure they fulfill that role for everyone, including low- and moderate-income communities and communities of color," said John Taylor, president and CEO of the National Community Reinvestment Coalition (NCRC), the driving force behind the recent proliferation of bank CBAs. In this incarnation of CBAs, banks team up with local community organizations to negotiate key services and resources targeted to communities traditionally underserved by banks.
In 2016, NCRC worked with hundreds of local community organizations to negotiate three large merger-related CBAs with Huntington Bank, KeyBank, and Fifth Third Bank. Collectively, these three agreements will bring $62.6 billion in lending and investments targeted to low- and moderate-income communities and communities of color across 23 states.
Reversing systematic disinvestment in low-income communities and communities of color
Bank CBAs capitalize on the Community Reinvestment Act (CRA) — a longstanding federal policy designed to encourage banks to meet the needs of moderate- and low-income neighborhoods. The CRA was passed in 1977 in an attempt to combat redlining — a destructive and discriminatory lending practice that denied or severely restricted access to mortgages, credit, and other financial resources necessary to promote economic growth within communities of color.
"The CRA has certain pressure points where communities have an opportunity to advocate for their needs," said Thomas Keily, consumer data and research coordinator at the Western New York Law Center, one of the grassroots NCRC members involved in the KeyBank CBA. Mergers, acquisitions, and CRA exams are intervention points where banks enter regulatory review and may be amenable to negotiations with community advocates.
Because bank mergers often result in branch closings that cut jobs and can reduce access to banking in certain locations, the CRA encourages banks to commit resources to counteract negative community ramifications. Traditionally, however, banks have sought to meet their CRA requirements without ongoing engagement with community leaders. The recent spate of bank-merger CBAs represents an important departure from business as usual.
Through a combination of in-person meetings, site visits, and conference calls, banks and representatives from several dozen community organizations negotiate the details of these agreements over the course of months. The resulting contracts include a wide range of commitments targeted to low-to-moderate income areas.
For example, the hundred-plus community partners representing six cities that came to the table to negotiate the Huntington Bank CBA identified four key focus areas for investment: affordable housing, workforce development, small business development, and supportive services, including community needs not typically associated with financial products, such as social services.
"The goal was to create a plan that was holistic and considered all the assets needed for a community to thrive and for individuals to reach their potential within that community," said Catherine Crosby, executive director of the City of Dayton's Human Relations Council, one of the organizations representing Dayton, Ohio, in the Huntington Bank negotiations. She is also a member of the NCRC board.
The resulting community development plan committed $5.7 billion in funding for single-family mortgages in low- and moderate-income areas and to low- and moderate-income borrowers, $3.7 billion in community development lending and investment for affordable housing, $25 million in grants for housing and small business credit services, and 10 new branch locations in underserved areas, among other investments. As this plan is implemented at the local level, community advocates have the opportunity to specify particular service needs within their local areas, such as down-payment assistance, loan counseling, or diversity requirements in bank hiring.
The CBA investments for KeyBank, announced in March 2016, contained similar measures, committing $16.5 billion in investments and lending over five years. The most recent CBA with Fifth Third Bancorp, announced in November 2016, represents the largest investment by a single bank in recent history — $30 billion invested across 10 states through 2020.
"The impact of billions of dollars in community reinvestment that comes from bank agreements cannot be overstated — the resources have a real, tangible impact, creating jobs and expanding access to mortgages, small business lending, education opportunities, and access to other financial resources," Taylor said.
The changes these CBAs are intended to implement come at a crucial time for Fifth Third. Earlier this month, the Federal Reserve released an assessment of the bank's 2011-2013 operations that found evidence of discriminatory practices during that time. As a result, Fifth Third's CRA compliance rating was lowered to "needs to improve."
Leveraging CBAs for equitable growth
Access to basic financial products and services — including bank accounts, mortgages, and retirement accounts — is a crucial component of building long-term financial security. Without these services, many families and individuals living paycheck to paycheck must turn to payday lenders and check-cashing centers that impose exorbitant interest rates and fees on those who can least afford it. According to a study conducted in California, payday lenders are nearly eight times as concentrated in primarily African American and Latino neighborhoods compared to White neighborhoods, draining nearly $247 million in fees from these communities each year.
"In Buffalo, New York, we've seen a systematic flight of financial resources within low-income communities and communities of color, especially in the city's east side," said Keily. "East of Main Street there are seven bank branches, but to the west there are over 25, and we see huge racial disparities in who gets mortgages."
On a community level, access to capital to purchase homes, start new businesses, or take on community development projects is a necessary ingredient for spurring economic growth, yet the majority of disinvested communities are still systematically underserved by the banks that could be providing these services. This persistent legacy of disinvestment perpetuates poverty and stymies the kind of growth that could revive local economies.
Through the CBA negotiation process, however, communities have increased leverage to hold financial institutions accountable for providing them with the services and resources that will enable them to thrive.
"This process gives community members back their voice and keeps their needs at the forefront of the process," said Keily. As part of negotiations with KeyBank, Western New York Law Center enlisted 100 residents to write about their experiences with financial institutions — testimonials that helped bring lived experience to the data and research presented during CBA meetings. The organization is also working to establish CBA agreements with smaller local banks and recently announced a $101.2 million agreement between the Northwest Savings Bank and Buffalo Niagara Community Reinvestment Coalition (BNCRC), a NCRC community-based coalition member.
As these agreements become increasingly popular, more and more banks are recognizing the value of working in concert with community to increase services and facilities in underserved markets.
"Some leaders of banks are stepping up and doing the work we also need to see from our political leadership — building collaborations between bank leaders, community group leaders like our members, and other stakeholders to ensure that communities have economic opportunity," Taylor said.
Delivering community benefits through broad coalitions
Negotiating the competing priorities of hundreds of community partners while attempting to influence large financial institutions that hold all the purse strings is no simple matter.
"NCRC did yeoman's work to bring everyone together," said Crosby. "A negotiation with this many parties is a push-and-pull process, so you need to have people who are thinking of the highest and greatest good for the community — not just themselves or their particular organizations."
But she felt the outcomes were well worth the laborious process.
"Formerly, the Human Relations Council would meet with the CRA officers for the bank to negotiate community investments, but this process is far more comprehensive and more impactful," Crosby said. There is also a key level of accountability, because communities can report to CRA regulatory bodies if a bank fails to make good on the promises encoded in the CBA.
Though it's too early in the implementation process to quantify the impact of these commitments, Crosby noted that the relationships formed and strengthened between the community partners that came together these past months have already been a huge win. Keily emphasized the power of the process for raising community awareness and empowerment.
"This shows us — and the community — what's possible when their voices are heard," he said. "It will be an ongoing process to implement this locally, but we're committed to keeping community members at the forefront of this process."